Difference between revisions of "User's manual"
(→Statistics) |
(→Proportional statistics) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
[[File:singleWords.png]] | [[File:singleWords.png]] | ||
| − | Words are searched by the criteria entered by the means of the large input field. In the above example, two criteria were selected: ''CVB (grammar)'' and ''VRB (POS)''. This search would return all the words from the database, which are annotated as CVB on the level grammar and as VRB on the level POS and possibly annotated also by other tags. In order to add a search criterion, start typing tag name in the input field, choose one from a pop-up list and press ENTER. The criterion will appear below the search field (as in the picture). To delete a criterion, just click on it. You may also specify | + | Words are searched by the criteria entered by the means of the large input field. In the above example, two criteria were selected: ''CVB (grammar)'' and ''VRB (POS)''. This search would return all the words from the database, which are annotated as CVB on the level grammar and as VRB on the level POS and possibly annotated also by other tags. In order to add a search criterion, start typing tag name in the input field, choose one from a pop-up list and press ENTER. The criterion will appear below the search field (as in the picture). To delete a criterion, just click on it. You may also specify if the searched words should appear as the first word in the sentence or be located in the middle of the sentence. Simply use an appropriate button in the section "Position in sentence". |
Search results are presented as follows: | Search results are presented as follows: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:SingleWordsFound.png]] |
| − | At the top of the results page you can see a filter. With the help of the filter you may narrow your search results to only show words from documents in a specific language(s) and/or coming from a specified epoque(s). At all times you may return to the default filter settings by choosing the option "any", both for language and epoque. | + | At the top of the results page you can see a filter. With the help of the filter you may narrow your search results to only show words from documents in a specific language(s) and/or coming from a specified epoque(s). Also, you can filter by individual documents. At all times you may return to the default filter settings by choosing the option "any", both for language and epoque. |
Below the filter you can see information about the total number of found words. Words are displayed in a table below in portions of 15 words per page. You can switch pages by using the buttons "first", "previous", "next" and "last". | Below the filter you can see information about the total number of found words. Words are displayed in a table below in portions of 15 words per page. You can switch pages by using the buttons "first", "previous", "next" and "last". | ||
| Line 162: | Line 162: | ||
In this case we take all words annotated as nouns and compute, how many nouns are furtherly tagged as singular, feminine. We obtain the following results: | In this case we take all words annotated as nouns and compute, how many nouns are furtherly tagged as singular, feminine. We obtain the following results: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:proportionalResults2.png]] |
| − | You can narrow the search by language | + | You can narrow the search by language, epoque and individual documents, just like any other set of results. In this case, however, you only get the numbers of word forms. |
Please note that in proportional statistics you can also specify if counted words are in initial position in the sentence. You can, for example, compute the percentage of all feminine nouns in initial position in the sentence within the set of all nouns. In order to make it work, you put in the "noun" tag into the "main search criteria" and select "any" as the "position in sentence". As the "additional specific criteria" you enter the "feminine" tag and select "initial" as "position in the sentence". However, not all such combinations are correct. You can't, for example, compute the percentage of feminine nouns in non-initial position within all nouns in initial position. If you enter sentence position criteria which are conflicting in this way, the "position in sentence" in the "main search criteria" will be automatically set to "any". | Please note that in proportional statistics you can also specify if counted words are in initial position in the sentence. You can, for example, compute the percentage of all feminine nouns in initial position in the sentence within the set of all nouns. In order to make it work, you put in the "noun" tag into the "main search criteria" and select "any" as the "position in sentence". As the "additional specific criteria" you enter the "feminine" tag and select "initial" as "position in the sentence". However, not all such combinations are correct. You can't, for example, compute the percentage of feminine nouns in non-initial position within all nouns in initial position. If you enter sentence position criteria which are conflicting in this way, the "position in sentence" in the "main search criteria" will be automatically set to "any". | ||
| Line 170: | Line 170: | ||
=== Predefined statistics === | === Predefined statistics === | ||
| − | The Tagger system comes with a set of predefined statistics. If some statistics are often generated, it is convenient to have their search criteria stored. In order to add a new predefined statistic to the list, please contact the system administrator. | + | The Tagger system comes with a set of predefined statistics. If some statistics are often generated, it is convenient to have their search criteria stored and generate them with a single click. In order to add a new predefined statistic to the list, please contact the system administrator. |
The predefined statistics list also includes two useful reports: words with "add info" and sentences with "add info". They are used to present words or sentences which were annotated on the "add info" level. This level is often used to enter comments about annotations to be read by other users. | The predefined statistics list also includes two useful reports: words with "add info" and sentences with "add info". They are used to present words or sentences which were annotated on the "add info" level. This level is often used to enter comments about annotations to be read by other users. | ||
Latest revision as of 22:11, 6 April 2017
Contents
User roles
Each user has a role in the system: reader, editor or administrator:
- Reader – may view documents
- Editor – may edit the documents (Section 6).
- Administrator – has access to configuration (Section 7).
Roles are assigned to users by administrator.
Getting started
System can be accessed from: IA tagger home DiaDef home
It requires: Chrome, Opera or Mozilla Firefox. To start, log in. The default password is tagger, which can be changed at any time.
| login | <request login from administrator> |
| password | tagger |
How to upload a text document
Select Documents. Click File/Wybierz dokument to select a text document that should be uploaded. In the Language window select the language of the document. Click Submit, to confirm the choice of the file and the language. The name of the file will be added to the list of documents uploaded so far (Documents list).
During the upload, the text is split into sentences and words. One line corresponds to one sentence. A string of characters between spaces is interpreted as a word.
How to open a document
Select the Documents option and click the name of the document from the list (or the adjacent icon).
How to save a document
You don’t have to save the document. Each modification is automatically saved.
How to annotate a document
An opened document is split into sentences. Sentences which already have some annotations are denoted as started with the icon ![]() . Click
. Click ![]() next to the sentence you want to annotate. You can navigate between sentences using CTRL + arrow (up or down).
next to the sentence you want to annotate. You can navigate between sentences using CTRL + arrow (up or down).
Adjusting the sentence splitting
You can adjust the automatic sentence splitting. Switch on the Edit mode (just below the menu). You can split the sentences with the scissors icon (![]() ) or merge them with the glue icon (
) or merge them with the glue icon (![]() ).
).
Editing the contents of a sentence
You can modify a sentence by adding or deleting words. Click any word in a sentence. You will see the following icons:
-
 - insert a new word before the current one - available for all words, which are not postpositions
- insert a new word before the current one - available for all words, which are not postpositions -
 - add a new word after the current one - available only for the last word
- add a new word after the current one - available only for the last word -
 - remove the word (available only for words that do not have postpositions; to remove a word that has a postposition, you must first separate it from the postposition)
- remove the word (available only for words that do not have postpositions; to remove a word that has a postposition, you must first separate it from the postposition) -
 - or (Ctrl-y) - mark the next word as a postposition (available only for words that do not have postpositions, are not postpositions themselves and do not end the line)
- or (Ctrl-y) - mark the next word as a postposition (available only for words that do not have postpositions, are not postpositions themselves and do not end the line) -
 - or (Ctrl-u) - separate the word from the postposition (available only postpositions or words having postpositions).
- or (Ctrl-u) - separate the word from the postposition (available only postpositions or words having postpositions).
Word breaking
Words can be split into a stem and a suffix: Click the word, select the position of the split with the mouse and press Ctrl-J. Confirm with Enter. To remove the split press Ctrl-K and confirm with Enter.
Word annotation
Words can be annotated at six different levels (levels can be set in Configuration menu, Section 7). To annotate a word at the selected level click on the level under the word you annotate.
Annotation levels
- LEXEME = equivalent English gloss
- GRAMMAR = grammatical role.
Type the starting character(s) of the tag and you will see the list of all tags beginning with the typed characters. For example: typing the ‘f’ character displays three tags starting with ‘f’: F (feminine), FOC (focus), FUT (future); typing the „pr” string displays six tags starting with „pr”. Click the tag from the list to annotate the word. - OTHER LEVELS
Annotation at other levels consists in selecting one or more suggestions offered by the system. To select or deselect the offered suggestion click it or press the shortcut button (given in the brackets). Moving to another edit box or pressing enter saves the value of the current edit box.
Sentence annotation
Sentences are annotated at two levels (levels are set up in the Configuration menu, Section 7): Add info (additional information) and English (English translation). At both levels sentences are annotated manually.
Tags suggested by the system
The suggestion cloud
Tagger suggests tags for words that fulfil one of the conditions:
- The same word has already occurred in one of the documents and has been tagged.
- The structure of the word allows the system to automatically deduce its tags.
Suggestions for tags appear in a cloud above the word. At most three suggestion lines may appear for one word. Each line suggests tags for a fee levels. For an instance, the suggestions for the word nagari looks as follows:
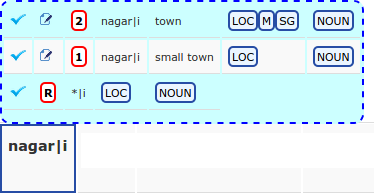
In the above example, the first 2 suggestions are generated according to annotations already existing in the system. By clicking the edit icon you can go to the word that was used to generate the suggestion. The number in the red border is the suggestion frequency score. It corresponds to the number of words in the system annotated with the tags of the suggestion.
The third suggestion in the example is marked with the letter R in a red border. This means that it was generated according to predefined rules. The rule used to generate this suggestion is "*|i". It catches words with the suffix "i" and suggests to annotate them as nouns in the locative case.
You can accept a chosen suggestion by clicking the ‘check’ symbol on the left side of a cloud or by using keyboard shortcuts CTRL + 1, CTRL + 2 or CTRL + 3. Accepting the first suggestion (shortcut CTRL + 1) would add the following tags to the annotation:
| Level | Tags |
|---|---|
| LEXEME | town |
| GRAMMAR | LOC, M, SG |
| POS | NOUN |
Tags overwritten by suggestions
Note that if the word for which the suggestions were generated had already been annotated, the suggested tags would overwrite existing annotations on corresponding levels. Original annotations on the levels which are absent in the suggestion are left untouched after applying this suggestion. In the above example, let us suppose that the word nagari already has the following annotations:
| Level | Tags |
|---|---|
| GRAMMAR | INS |
| SEM | REC |
If we now apply the first suggestion, the tag INS on the level GRAMMAR will be overwritten with 3 tags: LOC, M and SG, while the tag REC on the level SEM will be left untouched.
Exporting to Word
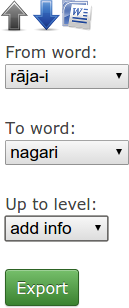
Tagger offers a feature of exporting a single table to a .docx document, a format used by Microsoft Word since the version MS Word 2007. In order to export a table or its part to Word, click the MS Word logo ![]() , which appears above the table right next to the up and down arrows. After clicking the button, the following export menu will pop up:
, which appears above the table right next to the up and down arrows. After clicking the button, the following export menu will pop up:
In the menu you may select the start and end word of the fragment to be exported. You can also set the maximum level of the annotations in the resulting Word document. After clicking the Export button, a document is generated and immediately downloaded.
The CTRL + z
The system allows for reverting recent editing changes by the means of a well known shortcut CTRL + z. Also, redoing an undone operation is possible via the shortcut CTRL + b. Be aware, however, of the following facts:
- Undoing and redoing only work when NOT in edit mode, i.e. when no cell is currently surrounded by red borer and edited.
- Deleting a word is the only operation which can not be undone!
- Applying a suggestion from the suggestion cloud and copying annotations from surrounding words are considered single operations, even if they modify multiple table cells.
- In order to make the undoing/redoing possible, the system maintains a history of operations. This history is deleted (making any undoings/redoings impossible) when:
- a user navigates to another sentence,
- a user logs out or closes the browser.
Statistics
The statistics module allows for generation of custom reports and statistics based on the annotations collected in the system. There are 3 basic types of statistics, which will be described in this section.
Single words
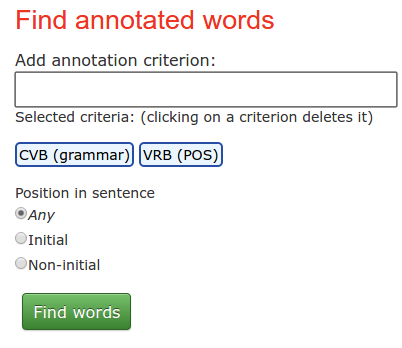
Single word search is configured by the following panel:
Words are searched by the criteria entered by the means of the large input field. In the above example, two criteria were selected: CVB (grammar) and VRB (POS). This search would return all the words from the database, which are annotated as CVB on the level grammar and as VRB on the level POS and possibly annotated also by other tags. In order to add a search criterion, start typing tag name in the input field, choose one from a pop-up list and press ENTER. The criterion will appear below the search field (as in the picture). To delete a criterion, just click on it. You may also specify if the searched words should appear as the first word in the sentence or be located in the middle of the sentence. Simply use an appropriate button in the section "Position in sentence".
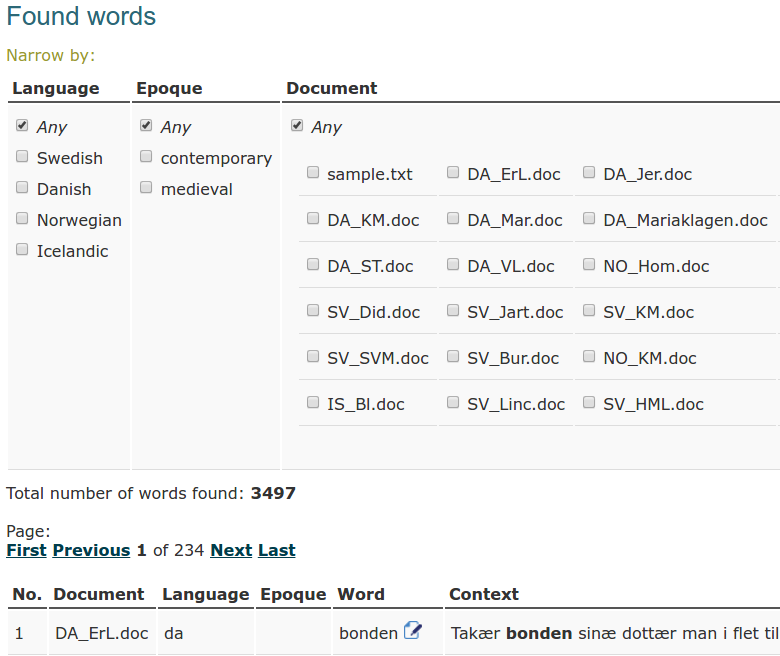
Search results are presented as follows:
At the top of the results page you can see a filter. With the help of the filter you may narrow your search results to only show words from documents in a specific language(s) and/or coming from a specified epoque(s). Also, you can filter by individual documents. At all times you may return to the default filter settings by choosing the option "any", both for language and epoque.
Below the filter you can see information about the total number of found words. Words are displayed in a table below in portions of 15 words per page. You can switch pages by using the buttons "first", "previous", "next" and "last".
Collocations
The second type of statistics are collocations. To search for collocations, you must specify two sets of search criteria (in exactly the same way as in single words search). The search results will display sentences containing at least one word conforming to the first set of search criteria and at least one word conforming to the second set.
Proportional statistics
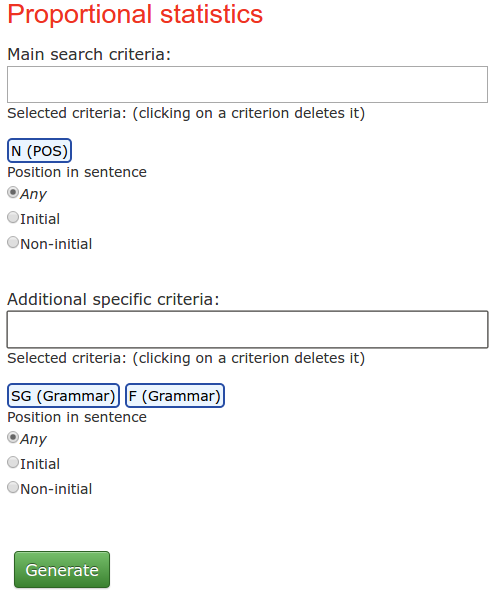
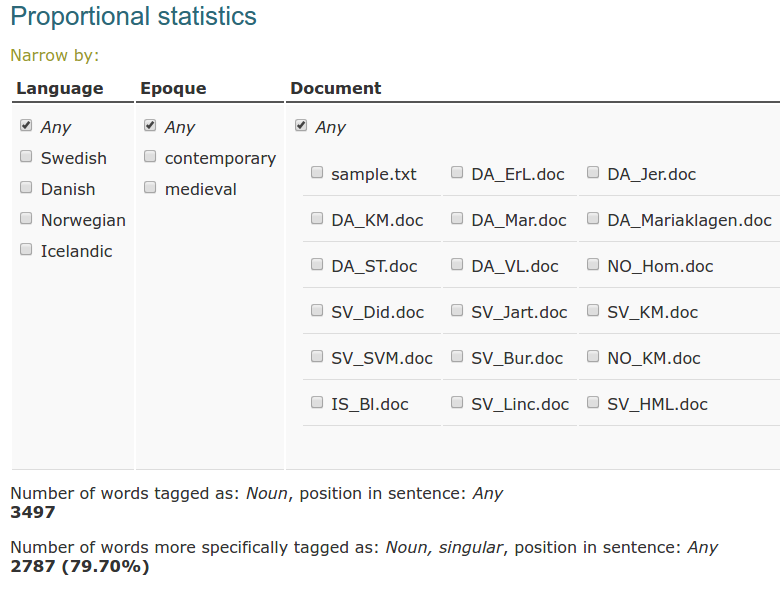
With the help of proportional statistics, you can compute the percentage of specific word forms in a set of all word forms of the same type. Consider the following example:
In this case we take all words annotated as nouns and compute, how many nouns are furtherly tagged as singular, feminine. We obtain the following results:
You can narrow the search by language, epoque and individual documents, just like any other set of results. In this case, however, you only get the numbers of word forms.
Please note that in proportional statistics you can also specify if counted words are in initial position in the sentence. You can, for example, compute the percentage of all feminine nouns in initial position in the sentence within the set of all nouns. In order to make it work, you put in the "noun" tag into the "main search criteria" and select "any" as the "position in sentence". As the "additional specific criteria" you enter the "feminine" tag and select "initial" as "position in the sentence". However, not all such combinations are correct. You can't, for example, compute the percentage of feminine nouns in non-initial position within all nouns in initial position. If you enter sentence position criteria which are conflicting in this way, the "position in sentence" in the "main search criteria" will be automatically set to "any".
Predefined statistics
The Tagger system comes with a set of predefined statistics. If some statistics are often generated, it is convenient to have their search criteria stored and generate them with a single click. In order to add a new predefined statistic to the list, please contact the system administrator.
The predefined statistics list also includes two useful reports: words with "add info" and sentences with "add info". They are used to present words or sentences which were annotated on the "add info" level. This level is often used to enter comments about annotations to be read by other users.
System configuration
The configuration of the system can be set solely by the administrator - other users don’t have access to configuration options.
By clicking Configuration you can manage the following options:
Users
This option allows to manage system users. You can add a new user (+ Add user) or delete a user (Delete). You can assign or change a role of the user (Change Role). You can reset the user’s system access password to a default password (Reset password), (e.g. when user forgets the password).
Languages
This option allows to manage languages of tagged documents. You can add a new language (+ Add language). The language will be added to the list of languages supported by the system. Once a new language is added, opening and tagging documents saved in this language becomes possible.
You can delete a chosen language (Delete) or edit it (Edit). Language edition allows you to change a language code (Code), which helps in shorter identification of the language, or to change the language description (Description).
Word annotation levels
This option allows you to manage the levels of word annotation. For each level you manage the following features:
- Name
- Description
- Strict Choices - if this option is selected (+), annotations on this level have the form of tags (e.g. POS), not text (e.g. LEXEME)
- Multiple Choice - if this option is selected (+) in addition to the above, tags for the words are chosen from a long list by their names (e.g. GRAMMAR)
Not selecting any of these options means that the word on this level should be annotated with text (e.g. LEXEME).
Levels are set in a pre-defined order. For example, by default the POS level is set as the first level. You may change the order of the levels by using arrows in the Order column. You can add a new level (+ Add word annotation level) or delete an existing level (Delete). You can edit the existing level (Edit), i.e. edit its name or the description, or modify Strict Choices and Multiple Choice.
For each level you can add or delete tags. To do so, you can use the option Edit tags. For each tag you should define its value (Value) and description (Description). In the process of tagging the editor may annotate words solely with tag values defined for each particular level.
You can change the order, in which tags are suggested to user. For example, for the POS level, the first suggestion on the list is the NOUN tag. You can move it to another position on the list by using arrows.
Sentence annotation level
This option allows you to manage levels of the sentence annotation, i.e. the levels, on which the Editor annotates whole sentences. Managing sentence annotation levels is similar to managing word annotation levels (word tags are not configured though).